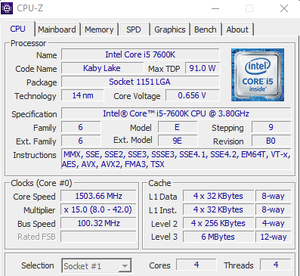
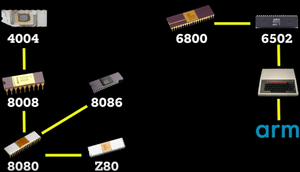
CPU
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Fairchild, Intel, Motorola, TI, MOS, Zilog, Sun, Dec, IBM, ARM
Fairchild IC's (traitorous eight) Intel 4004, 8008, 8088 Zilog Z80 Motorola 6800 MOS 6502 Acorn ARM
RISC Berkley / IBM MIPS Stanford IBM PowerPC SUN Sparc DEC Alpha
MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSSE3, SSE4.1, SSE4.2, EM64T, VT-x, AES, AVX, AVX2, FMA3, TSX
Moore's Law / Transistors
| Integration level | Year | Logic gates | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSI | Medium Scale Integration | 1976 | 20-200 | |
| LSI | Large‐scale integration | 1970 | 200-2000 | 10 µm |
| VLSI | Very large‐scale integration | 1980 | 2.000-20.000 | 1.5 µm |
| ULSI | Ultra large‐scale Integration | 1990 | 20.000-200.000 | 600 nm |
| SLSI | Super large‐scale integration | 2000 | 200.000- 2 million | 130 nm |
| 2010 | 2 million - 20 million | 22 nm | ||
| 2020 | 20 million - 200 million | 5 nm |
MIPS
1976: IBM 801 first conceptual RISC processor
1980: DARPA VLSI Project University funding
RISC Berkley (David Patterson)
MIPS Stanford University (John Hennessy)
1984 Company: MIPS Techology
1992 Acquired by SGI
1998 Divested
2013 Imagination (from PowerVR)
2022 Moved to RISC-V
Architecture and Licensing
Lexra
RISC
University of Berkeley project
1981 RISC I (44,500 transistors, 31 instructions, 78 32-bit registers)
RISC Foundation
2015 RISC V
ARM
OS (BSD/Linux/Windows etc): uses MMU Memory Management Unit
RTOS: Task scheduler.