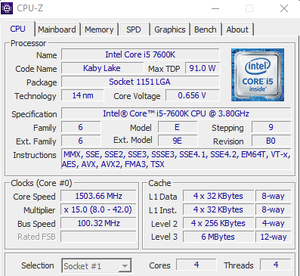
CPU
Super Computers
1943 ENIAC
EDVAC
BINAC
1951 UNIVAC
ORDVAC
UNIVAC
UNISYS
ILLIAC
EDSAC
Manchaster Baby
CTC Computer Terminal Corporation
Datapoint 3300
ERA Remington Rand UNIVAC
CDC
CRAY
1955: Shockley Semiconductor Laboratory (Caltech / MIT / Bell labs)
1957: Fairchild Semiconductor (traitorous eight)
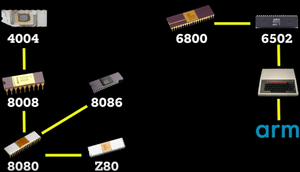
1968: Intel (Noyce and Moore)
1974: Zilog (Federico Faggin)
Z80 is a 5V spinoff from an Intel 8080
Now Littlefuse > IXYS > Zilog
Fairchild, Intel, Motorola, TI, MOS, Zilog, Sun, Dec, IBM, ARM
Fairchild IC's (traitorous eight) Intel 4004, 8008, 8088 Zilog Z80 Motorola 6800 MOS 6502 Acorn ARM
RISC Berkley / IBM MIPS Stanford IBM PowerPC SUN Sparc DEC Alpha
MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSSE3, SSE4.1, SSE4.2, EM64T, VT-x, AES, AVX, AVX2, FMA3, TSX
Moore's Law / Transistors
| Integration level | Year | Logic gates | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSI | Small Scale Integration | 1964 | ||
| MSI | Medium Scale Integration | 1968 | 20-200 | |
| LSI | Large‐scale integration | 1970 | 200-2000 | 10 µm |
| VLSI | Very large‐scale integration | 1980 | 2.000-20.000 | 1.5 µm |
| ULSI | Ultra large‐scale Integration | 1990 | 20.000-200.000 | 600 nm |
| SLSI | Super large‐scale integration | 2000 | 200.000- 2 million | 130 nm |
| 2010 | 2 million - 20 million | 22 nm | ||
| 2020 | 20 million - 200 million | 5 nm |
CISC v.s. RISC
RISC is a philosophy to use simpler instructions to achieve the same as complex instruction. For example for AES rowshifting an Intel can use XMM instructions to shift multiple rows in one operation, while RISC processors need to loop through the bytes and execute simpler instructions. It takes longer to execute, but without SIMD the processor is smaller, cheaper and wins in power efficiency.
Intel CISC
PCLMULHQHQDQ xmmreg,xmmrm
ARM RISC
result = operand1 EOR operand2;
for s = 0 to segments-1
Elem[result, s, 128] = AESSubBytes(AESShiftRows(Elem[result, s, 128]));
RISC
| University of Berkeley | Intended for research | |
| 1981 | RISC I | 44,500 transistors, 31 instructions, 78 32-bit registers |
| RISC Foundation | Open ISA free to implement | |
| 2015 | RISC V | |
MIPS
| 1976 | IBM 801 | first conceptual RISC processor |
| 1980 | DARPA VLSI Project University funding | |
| RISC | University of Berkley (David Patterson) | |
| MIPS | Stanford University (John Hennessy) | |
| 1984 | MIPS Computer Systems, Inc. | |
| 1992 | Acquired by SGI | |
| 1998 | SGI spun off MIPS | |
| 2008 | lost money on buying and selling Chipidea | |
| 2013 | bought by Imagination Technologies (PowerVR) | |
| 2022 | Adopted RISC-V |
| 1997 | Lexra based on MIPS-I instruction set (Not the core license) | |
| 1998 | Patent on "unaligned loads and stores" | |
| 2003 | Lexra bankrupt | |
| 2006 | RTL8196E | Realtek continues to use Lexra Cores (RLX4181) |
ARM
Cortex-A Microprocessors, with an MMU, for Rich OS e.g. BSD/Linux/Windows)
Cortex-R Realtime processors
Cortex-M Microcontrollers for RTOS Task Scheduling
ARMv7-M ISA
M0+ von neuman (instruction and data share the same bus)
M3
M4
M7
ARMv8-M
M23 Trustzone
M33
M35P
Armv8.1-MM55
M85
Segger
SEGGER J-Link EDU Mini - JTAG/SWD Debugger
https://thepihut.com/products/segger-j-link-edu-mini-jtag-swd-debugger