CPU: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→MIPS) |
(→RISC) |
||
| Line 86: | Line 86: | ||
2022 Moved to RISC-V | 2022 Moved to RISC-V | ||
| Line 93: | Line 94: | ||
=== RISC === | === RISC === | ||
University of Berkeley | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ | |||
1981 RISC I | ! | ||
! | |||
RISC Foundation | ! | ||
|- | |||
2015 RISC V | |University of Berkeley | ||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
|1981 | |||
|RISC I | |||
|44,500 transistors, 31 instructions, 78 32-bit registers | |||
|- | |||
|RISC Foundation | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
|2015 | |||
|RISC V | |||
| | |||
|} | |||
=== '''ARM''' === | === '''ARM''' === | ||
Revision as of 08:26, 17 November 2023
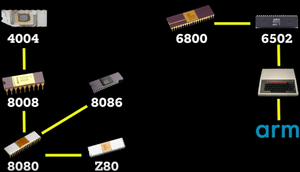
Fairchild, Intel, Motorola, TI, MOS, Zilog, Sun, Dec, IBM, ARM
Fairchild IC's (traitorous eight) Intel 4004, 8008, 8088 Zilog Z80 Motorola 6800 MOS 6502 Acorn ARM
RISC Berkley / IBM MIPS Stanford IBM PowerPC SUN Sparc DEC Alpha
MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, SSSE3, SSE4.1, SSE4.2, EM64T, VT-x, AES, AVX, AVX2, FMA3, TSX
Moore's Law / Transistors
| Integration level | Year | Logic gates | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSI | Medium Scale Integration | 1976 | 20-200 | |
| LSI | Large‐scale integration | 1970 | 200-2000 | 10 µm |
| VLSI | Very large‐scale integration | 1980 | 2.000-20.000 | 1.5 µm |
| ULSI | Ultra large‐scale Integration | 1990 | 20.000-200.000 | 600 nm |
| SLSI | Super large‐scale integration | 2000 | 200.000- 2 million | 130 nm |
| 2010 | 2 million - 20 million | 22 nm | ||
| 2020 | 20 million - 200 million | 5 nm |
MIPS
1976: IBM 801 first conceptual RISC processor
1980: DARPA VLSI Project University funding
RISC Berkley (David Patterson)
MIPS Stanford University (John Hennessy)
1984 Company: MIPS Techology
1992 Acquired by SGI
1998 Divested
2013 Imagination (from PowerVR)
2022 Moved to RISC-V
Architecture and Licensing
Lexra
RISC
| University of Berkeley | ||
| 1981 | RISC I | 44,500 transistors, 31 instructions, 78 32-bit registers |
| RISC Foundation | ||
| 2015 | RISC V |
ARM
OS (BSD/Linux/Windows etc): uses MMU Memory Management Unit
RTOS: Task scheduler.