Agile: Difference between revisions
(→SAFE) |
(→Scrum) |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
=== FORD Production Line === | === FORD Production Line === | ||
Model-T | Model-N 1906 Inexpensive entry level | ||
Model-T 1908 mass-affordable, in 1913 started the assembly line | |||
Model-A 1927 | |||
https://corporate.ford.com/articles/history/moving-assembly-line.html | |||
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rHXgdGSttU0&t=33s | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rHXgdGSttU0&t=33s | ||
[[File:Men-working-on-model-a-assembly-line.jpg|thumb|FORD Model A assembly line (1931)]] | |||
=== | === Toyota TPS === | ||
W. Edwards Deming | W. Edwards Deming in Japan | ||
TPS Toyota Production System | |||
[[File:P4-prodsystemvideo-Screenshot-2022-03-31-at-13.35.webp|thumb|TPS Andon]] | |||
https://global.toyota/en/company/vision-and-philosophy/production-system/ | |||
https://www.toyota-europe.com/about-us/toyota-vision-and-philosophy/toyota-production-system | |||
Bloomberg: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=F5vtCRFRAK0&t=66s | Bloomberg: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=F5vtCRFRAK0&t=66s | ||
| Line 16: | Line 30: | ||
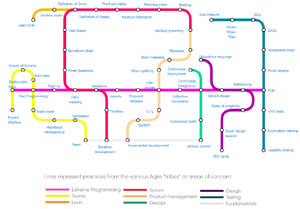
[[File:Agile Metro.png|thumb|Agile Metro Map]] | [[File:Agile Metro.png|thumb|Agile Metro Map]] | ||
https://kanbanzone.com/resources/lean/toyota-production-system/ | |||
Produce Just-in-time, reduce stock, Pull your own work, restock what’s needed | |||
Produce Just-in-time, reduce stock | |||
Kanban Visualize Work (backlog, todo, in progress, done) | '''Kanban''' Visualize Work Identify bottlenecks, Limit Work in Progress (backlog, todo, in progress, done) | ||
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R8dYLbJiTUE&t=25s | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R8dYLbJiTUE&t=25s | ||
'''Kaizen''': Continuous Improvement | |||
'''Jidoka''': Stop the line, Identify bottlenecks, Prevent defects, Don’t maximize production, if there are defects down the line | |||
Andon | |||
The Toyota Way | |||
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Toyota_Way | |||
=== Lean === | === Lean Manufacturing === | ||
Eliminate waste | Eliminate waste, Based on TPS / Motorola Six Sigma | ||
=== Agile Manifesto === | === Agile Software Development Manifesto === | ||
Individuals and interactions over processes and tools | Individuals and interactions over processes and tools | ||
| Line 77: | Line 90: | ||
At regular intervals, the team reflects on how to become more effective, then tunes and adjusts its behavior accordingly. | At regular intervals, the team reflects on how to become more effective, then tunes and adjusts its behavior accordingly. | ||
=== | === SAFe === | ||
[[File:SAFE6.png|thumb|SAFE6]] | [[File:SAFE6.png|thumb|SAFE6]] | ||
Agile | Scaled Agile Framework for enterprise | ||
https://scaledagileframework.com/# | |||
=== Scrum === | === Scrum === | ||
| Line 86: | Line 101: | ||
PO: Understands customer requirements | PO: Understands customer requirements | ||
Scrum Master: Facilitates the team | Scrum Master: Facilitates the team, organize scrum events, assign accountability, create artifacts | ||
https://scrumguides.org/scrum-guide.html#scrum-master | |||
[[File:Scrum.png|thumb|Scrum]] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:11, 15 February 2024
Spotify Engineering Culture
Henrik Kniberg, Spotify Engineering Culture (1 and 2)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4GK1NDTWbkY
FORD Production Line
Model-N 1906 Inexpensive entry level
Model-T 1908 mass-affordable, in 1913 started the assembly line
Model-A 1927
https://corporate.ford.com/articles/history/moving-assembly-line.html
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rHXgdGSttU0&t=33s
Toyota TPS
W. Edwards Deming in Japan
TPS Toyota Production System
https://global.toyota/en/company/vision-and-philosophy/production-system/
https://www.toyota-europe.com/about-us/toyota-vision-and-philosophy/toyota-production-system
Bloomberg: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=F5vtCRFRAK0&t=66s
https://kanbanzone.com/resources/lean/toyota-production-system/
Produce Just-in-time, reduce stock, Pull your own work, restock what’s needed
Kanban Visualize Work Identify bottlenecks, Limit Work in Progress (backlog, todo, in progress, done)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R8dYLbJiTUE&t=25s
Kaizen: Continuous Improvement
Jidoka: Stop the line, Identify bottlenecks, Prevent defects, Don’t maximize production, if there are defects down the line
Andon
The Toyota Way
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Toyota_Way
Lean Manufacturing
Eliminate waste, Based on TPS / Motorola Six Sigma
Agile Software Development Manifesto
Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
Working software over comprehensive documentation
Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
Responding to change over following a plan
Agile Principles
https://www.agilealliance.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/Subway-Map-to-Agile-Practices.pdf
Our highest priority is to satisfy the customer through early and continuous delivery of valuable software.
Welcome changing requirements, even late in development. Agile processes harness change for the customer's competitive advantage.
Deliver working software frequently, from a couple of weeks to a couple of months, with a preference to the shorter timescale.
Business people and developers must work together daily throughout the project.
Build projects around motivated individuals.
Give them the environment and support they need, and trust them to get the job done.
The most efficient and effective method of conveying information to and within a development team is face-to-face conversation.
Working software is the primary measure of progress.
Agile processes promote sustainable development.
The sponsors, developers, and users should be able to maintain a constant pace indefinitely.
Continuous attention to technical excellence and good design enhances agility.
Simplicity--the art of maximizing the amount of work not done--is essential.
The best architectures, requirements, and designs emerge from self-organizing teams.
At regular intervals, the team reflects on how to become more effective, then tunes and adjusts its behavior accordingly.
SAFe
Scaled Agile Framework for enterprise
https://scaledagileframework.com/#
Scrum
https://www.scrum.org/resources/what-scrum-module
PO: Understands customer requirements
Scrum Master: Facilitates the team, organize scrum events, assign accountability, create artifacts https://scrumguides.org/scrum-guide.html#scrum-master