Charset: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
=== Codepages === | === Codepages === | ||
8 bit, lower half 0000000-011111111 is compatible with ASCII | |||
IBM | IBM / Windows CodePages: Windows-1252 (defines the C1) | ||
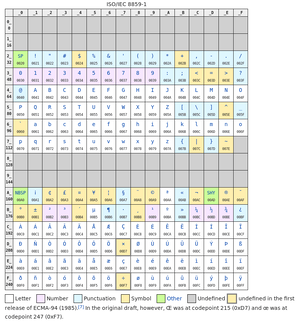
[[File:Latin-1.png|thumb]] | |||
ISO-8859-1 Latin-1 (leaves C1 empty, upper half contains regionally significant characters) | |||
ISO-8895-2 Latin-2 upper half is mostly for slavic languages | |||
ISO- | |||
https://www.charset.org/charsets/iso-8859-1 | https://www.charset.org/charsets/iso-8859-1 | ||
| Line 37: | Line 38: | ||
UTF 8 bit | |||
UTF-8 is 8 bit | |||
0bbbbbbb => us-ascii | 0bbbbbbb => us-ascii | ||
Revision as of 09:44, 19 July 2024
Unicode isn't hard if you know the history and where it comes from
https://mcilloni.ovh/2023/07/23/unicode-is-hard/
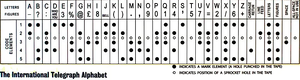
Teleprinter / TelegrafBaudot Encoding 5-bit, ITA-1
https://cryptii.com/pipes/baudot
International Encoding
ITU-T T50 IA5 String
https://www.itu.int/rec/T-REC-T.50
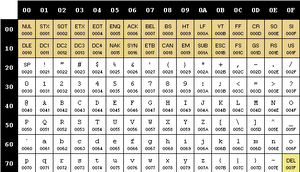
ASCII 7-bit C0 set of Control Characters / G0 set of Graphic Characters
Codepages
8 bit, lower half 0000000-011111111 is compatible with ASCII
IBM / Windows CodePages: Windows-1252 (defines the C1)
ISO-8859-1 Latin-1 (leaves C1 empty, upper half contains regionally significant characters)
ISO-8895-2 Latin-2 upper half is mostly for slavic languages
https://www.charset.org/charsets/iso-8859-1
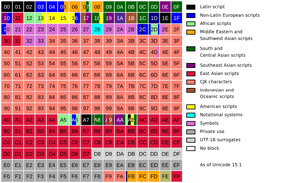
Unicode
upper codepoints used for Unicode 2-byte UCS-2 or 4-byte UCS-4
EURO SIGN: U+20AC
https://www.fileformat.info/info/unicode/char/20ac/index.htm
UTF-8 is 8 bit
0bbbbbbb => us-ascii
10bbbbbb => next byte is also part of the character (character is up to 6 bytes)
Byte order BOM FFFE
HTML Escaping
Java internal UCS-2